Introduction to Human body anatomy
Human body anatomy is the scientific study of the structure of the human body. It explains how the body’s organs, tissues, cells, and systems work together. Anatomy is a cornerstone of medical science, aiding healthcare professionals in diagnosing diseases, performing surgeries, and understanding the body’s responses to various conditions.
The human body is a complex and intricately designed system made up of several interdependent systems. These include the skeletal, muscular, nervous, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, endocrine, urinary, reproductive, and integumentary systems. Each system plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis, ensuring optimal function and survival.
The skeletal system forms the structural framework of the body, providing support, protection, and movement when paired with the muscular system. The nervous system acts as the body’s communication network, transmitting signals between the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. Meanwhile, the circulatory system ensures the distribution of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body while removing waste products.
Anatomical terminology is essential for clear communication among healthcare professionals. It uses standardized terms to describe body positions, directions, and planes, ensuring accurate and efficient information exchange. For instance, terms like anterior, posterior, lateral, and medial help describe the location of body structures relative to each other.
The study of human anatomy has evolved significantly over centuries. Early studies relied on dissections of cadavers, which laid the groundwork for modern anatomical knowledge. Technological advancements, such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans, have greatly enhanced our ability to explore the human body non-invasively.
Human anatomy is also fundamental to fields beyond medicine, including physical therapy, sports science, yoga, and fitness. For instance, yoga practitioners benefit from understanding anatomical structures like muscles, joints, and connective tissues to optimize posture, breathing techniques, and injury prevention.
Human body organ chart
The human body functions as an intricate system made up of essential organs that collaborate to sustain life. Grasping the structure and roles of these organs is crucial for overall health and well-being.
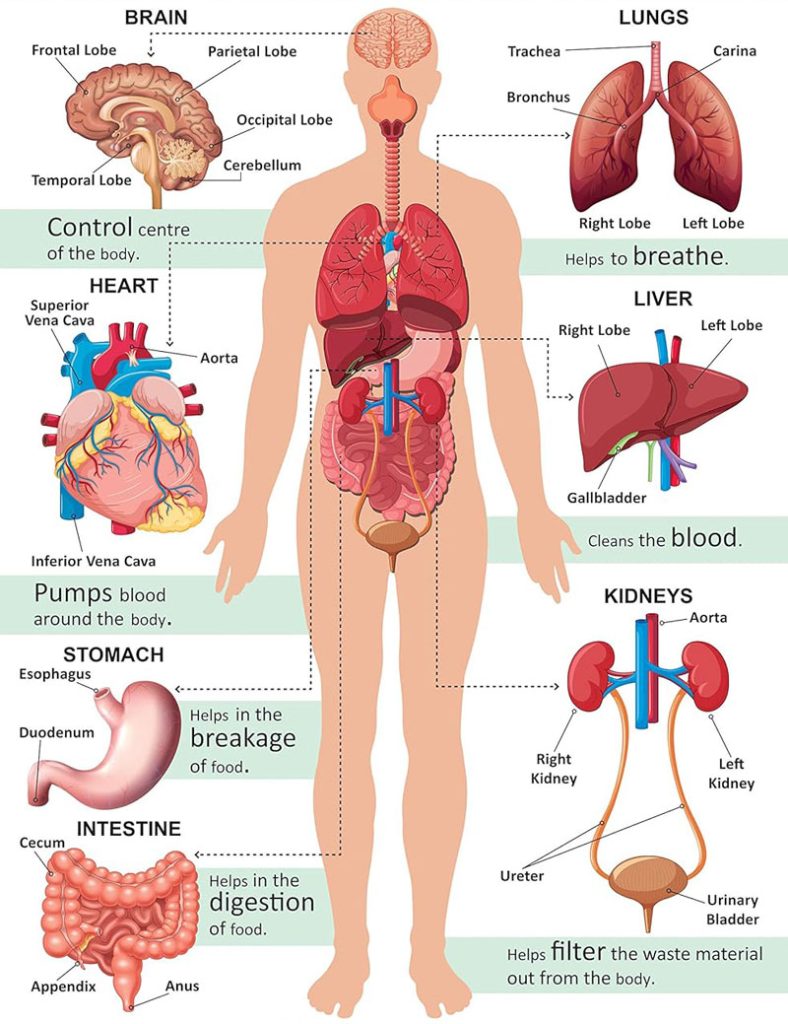
human body organs diagram Vital Organs and Their Functions
1. Brain
The brain serves as the body’s command center, overseeing thought processes, memories, emotions, and the regulation of bodily functions. It interacts through the nervous system and orchestrates movement.
2. Heart
The heart circulates oxygen-rich blood throughout the body via the cardiovascular system, beating around 100,000 times daily to ensure cells receive necessary oxygen and nutrients.
3. Lungs
The lungs enable respiration by exchanging oxygen for carbon dioxide. They collaborate closely with the heart to provide the body with oxygenated blood.
4. Liver
The liver purifies the blood, processes nutrients, and generates bile for digestion. It is vital in metabolizing fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
5. Kidneys
The kidneys filter out waste from the bloodstream and help regulate fluid balance, as well as maintaining electrolyte levels and blood pressure.
6. Stomach
The stomach utilizes acids and enzymes to break down food, preparing it for further digestion in the intestines.
7. Intestines (Small & Large)
The small intestine is responsible for nutrient absorption, while the large intestine focuses on waste elimination and water absorption.
8. Skin
As the largest organ, the skin provides a protective barrier and helps regulate body temperature.
In Summary
Every organ plays a unique part in supporting health. Recognizing their functions can guide you in making healthier lifestyle decisions. Maintain your well-being through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper hydration!
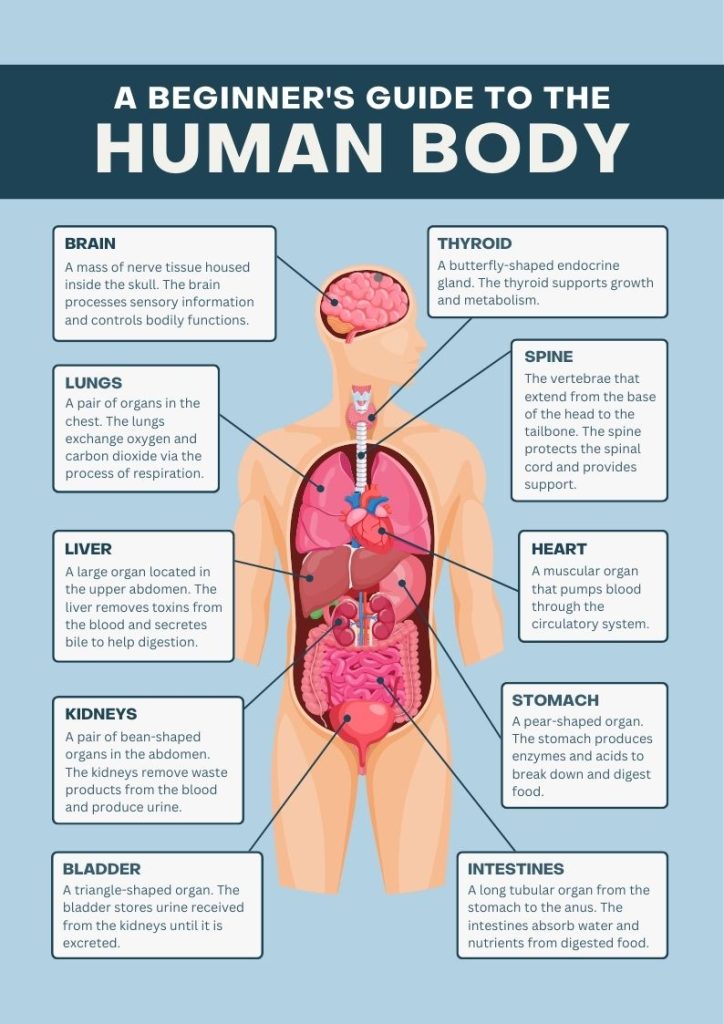
A picture of the Human body anatomy
Why is human anatomy class important going into microbiology
Understanding Human body anatomy is crucial for anyone studying microbiology. It helps explain how microorganisms interact with the body. Here are some reasons why anatomy matters in microbiology:
1. Understanding Organ Systems
Microbiology looks at how bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes affect different organs and tissues. Knowing human anatomy helps identify how infections spread and impact systems like the respiratory, digestive, or immune systems.
2. Understanding Disease Mechanisms
Many microorganisms cause diseases by targeting specific organs. For example, tuberculosis mainly affects the lungs, while hepatitis targets the liver. A strong grasp of anatomy helps microbiologists track disease progression and create effective treatment plans.
3. Immune System Function
Microbiology studies how the immune system responds to germs. Knowledge of anatomy highlights important immune organs like the spleen, bone marrow, and lymph nodes that help fight infections.
4. Applications in Medicine and Labs
Microbiologists often work with clinical samples such as blood, tissues, and bodily fluids. A basic understanding of anatomy is essential for accurately identifying these samples and interpreting lab results.
Does advanced human and comparative anatomy
Advanced human anatomy studies the body’s structures in detail, including both small (microscopic) and large (macroscopic) parts. This field looks closely at organ systems and tissues, often using medical imaging and dissection to gain a complete understanding.
Comparative anatomy examines the similarities and differences between human anatomy and that of other animals. This science helps researchers find evolutionary links, functional changes, and structural variations among species. For example, studying the skeletons of humans, primates, and other mammals reveals insights into movement and evolution.
A colorful introduction to the anatomy of the human brain
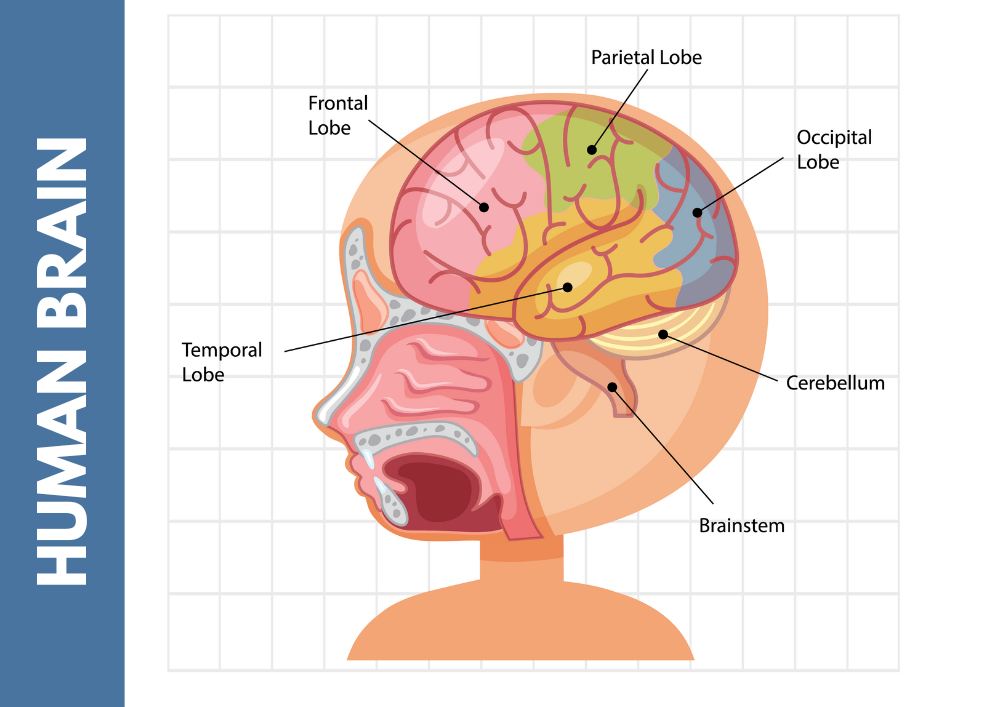
The human brain is a complex organ that controls thoughts, feelings, movements, and memories. It has different areas, each with specific functions, working together to process information and keep the body running smoothly.
Major Areas of the Brain:
🧠 Cerebrum – The largest part of the brain, responsible for reasoning, emotions, problem-solving, and voluntary actions. It has two hemispheres and four lobes:
– Frontal Lobe – Involved in decision-making and reasoning.
– Parietal Lobe – Responsible for touch and spatial awareness.
– Temporal Lobe – Related to hearing and memory.
– Occipital Lobe – Focused on vision.
🎯 Cerebellum – Located at the back of the brain, it helps with balance, movement coordination, and fine motor skills.
⚡ Brainstem – Connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls essential functions like breathing, heart rate, and reflexes.
🔍 Limbic System – Known as the emotional center of the brain, it includes the hippocampus (related to memory) and amygdala (linked to emotions).
Why Understanding Brain Structure Matters:
Knowing how the brain is structured helps us understand mental health issues, neurological disorders, and ways to improve cognitive skills. With its many neurons and complex connections, the brain is one of the most amazing organs in our body!
Diagram of male reproductive system to label
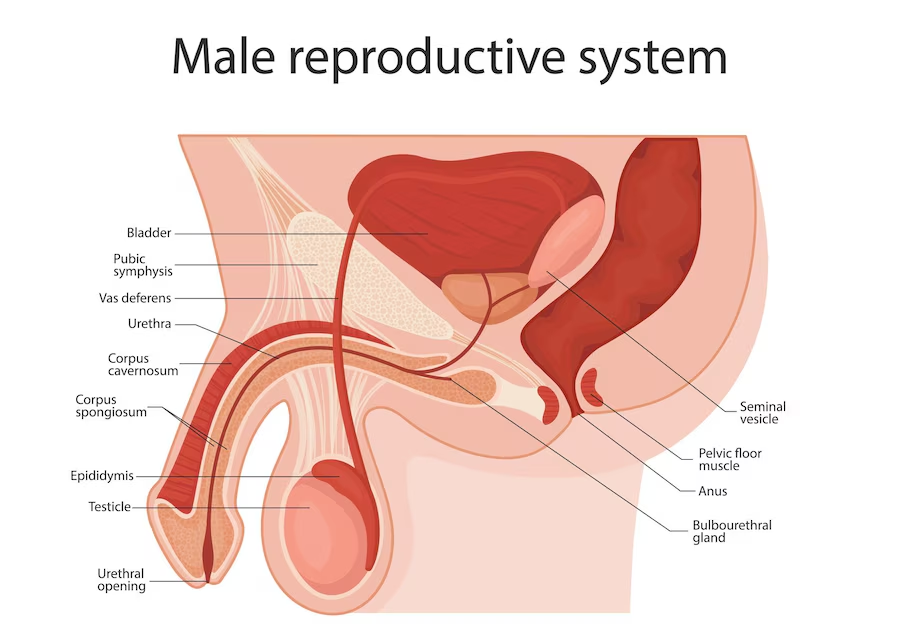
Here’s a list of key parts to label:
- Testes – Produce sperm and testosterone.
- Epididymis – Stores and matures sperm.
- Vas Deferens – Transports sperm from the epididymis.
- Seminal Vesicles – Produce seminal fluid for sperm nourishment.
- Prostate Gland – Secretes fluid to protect and nourish sperm.
- Urethra – Passage for urine and semen out of the body.
- Penis – External organ for urination and sperm delivery.
- Scrotum – Sac holding the testes, regulating temperature.
- Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper’s Glands) – Release fluid to lubricate the urethra.





